From Compass to ToF: How Humans Learned to Navigate & Understand Space
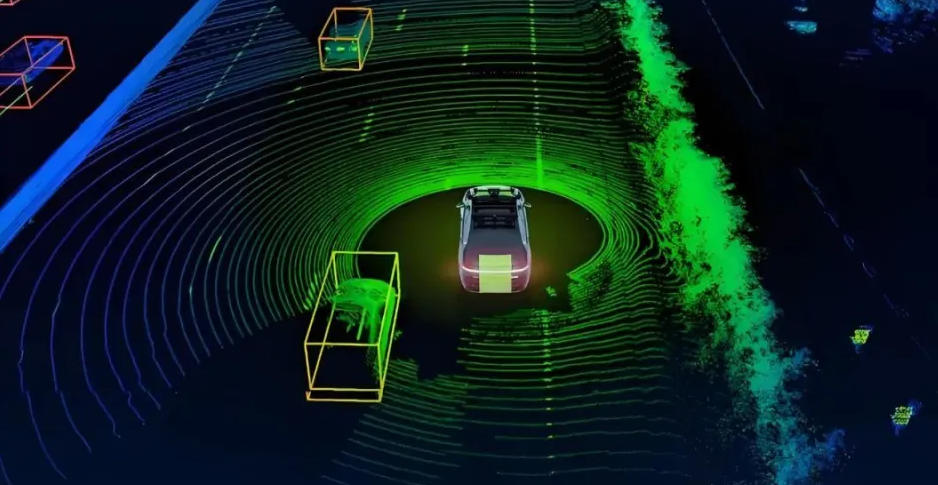
How Did Humans Navigate Before GPS and Evolve to Using ToF Technology?
Throughout the development of human civilization, 'how to determine direction and position' has always been one of the core drivers of technological progress. From the earliest compass and oldest maps to today’s 3D perception and autonomous navigation systems based on TOF (Time-of-Flight) technology, humanity’s understanding of space has undergone one revolutionary leap after another.
This article starts with the highly searched question 'when was the compass invented', systematically reviews the origin and history of the compass, and further extends to modern ToF technology, revealing the evolution of navigation from 'direction sensing' to 'spatial understanding.'
What is the formula for Time of Flight?
The core formula of Time of Flight (ToF) is used to calculate distance based on the signal’s travel time, as follows:
Basic ToF Formula
or written as:
Explanation of Symbols:
-
d: Distance between the target and the sensor
-
v: Signal propagation speed
-
Optical ToF: speed of light
-
Ultrasonic ToF: speed of sound ≈343 m/s (in air)
-
-
t: Round-trip time from signal emission to reflection and return
-
Division by 2: Because the measured time is the round-trip, but the distance is only for a one-way path
1. The Origin of the Compass: What Was the Oldest Compass in the World?
Where was the compass invented?
Historical and archaeological research generally recognizes China as the origin of the compass.
As early as the 4th–3rd century BCE, ancient Chinese people had discovered that natural magnets (magnetite) possess directional properties.
The earliest directional device was called:
-
Sinan
-
Shaped like a spoon, placed on a smooth bronze plate
-
The handle of the spoon always pointed south
This is widely considered the world’s oldest compass / earliest compass.
2. When Was the Compass Invented?
The question 'when was the compass invented?' has very high search volume globally. People often phrase it in different ways, such as when was compass invented, when were compasses invented, when was a compass made, or more specific long-tail queries like when was the first compass invented and when was the first compass made.
Historians generally agree that the earliest compass originated in ancient China during the Warring States period, when people used the natural properties of magnetite to indicate direction for navigation and other purposes. Over time, the compass spread worldwide, providing reliable directional reference for navigation, exploration, and early mapmaking. No matter how people search, the answer is basically the same: the compass was invented in ancient China and represents a major milestone in human navigation history.
Key Historical Milestones:
-
3rd century BCE (Warring States period):
Magnetic directional tools (prototype of Sinan) appear -
Northern Song Dynasty (~11th century CE):
Magnetic needle compasses are officially used in navigation -
12th–13th century CE:
Compass technology spreads to Europe via the Arab world
👉 Therefore, we can answer:
The compass was invented in ancient China more than 2,000 years ago.
3. Who Invented the Compass?
Unlike modern engineering inventions, the compass does not have a single inventor.
-
It was the result of long-term observation of natural magnetic phenomena
-
Gradually improved by ancient Chinese craftsmen, astronomers, and geomancers
-
Represents civilizational-level technological accumulation
Thus, the authoritative answer to who is the inventor of the compass is:
The compass has no single inventor; it is the collective wisdom of ancient China.






