Smart Gesture Control: Revolutionizing Interaction in Homes & Beyond
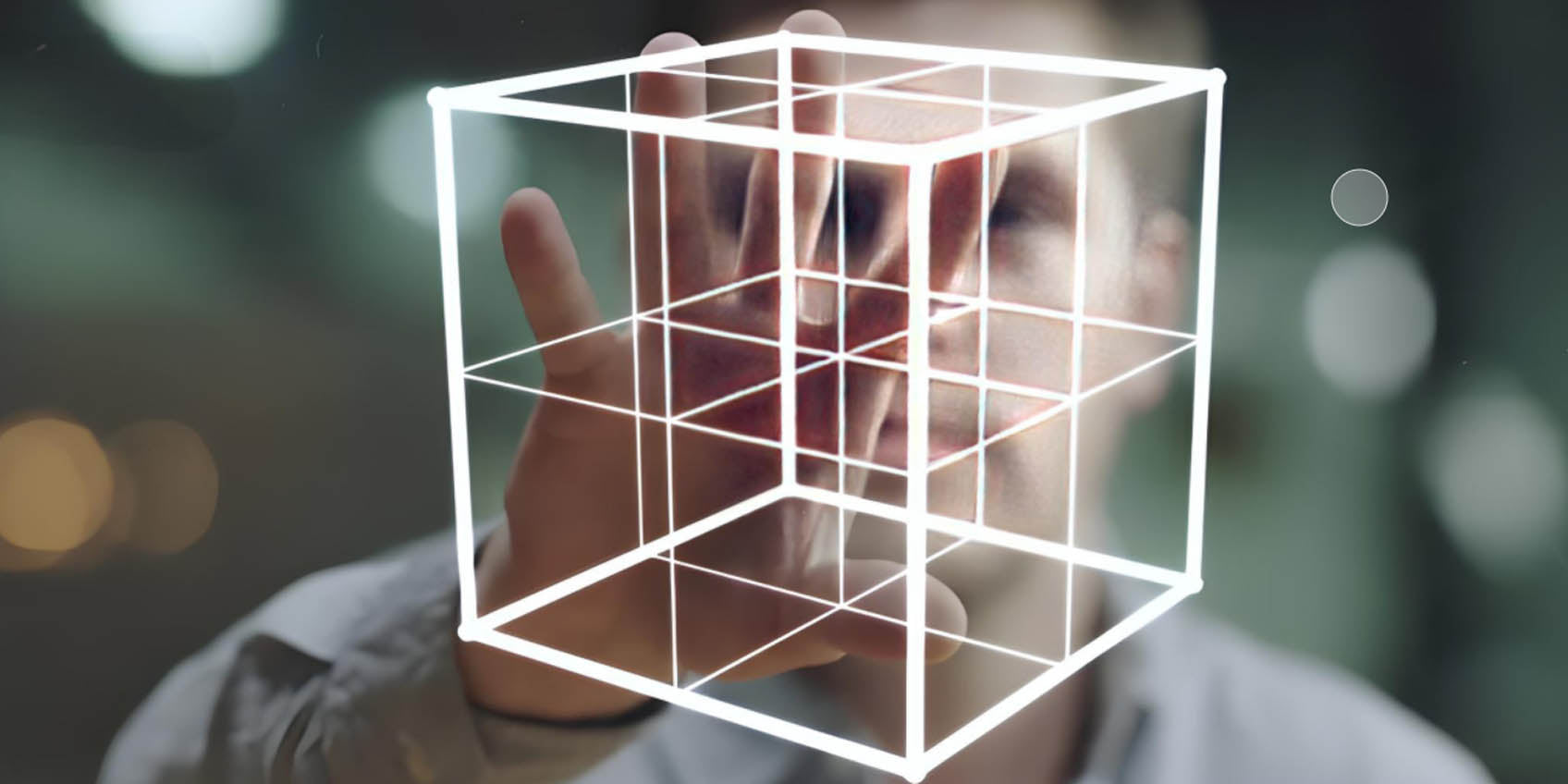
With the rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI), computer vision, deep learning, and sensor technologies, smart gesture control is making significant strides across numerous industries, including smart homes, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), gaming, security monitoring, and healthcare.
Traditional gesture recognition systems primarily relied on basic sensors and static algorithms, but smart gesture control now integrates cutting-edge technologies like LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), infrared sensors, and 3D vision recognition, enabling high precision, real-time control of user gestures with unprecedented accuracy and flexibility.
This evolution has transformed gesture control from a mere convenience to a fundamental component of digital transformation. Industries like industrial control, robotics, and healthcare now leverage this technology to enhance human-machine interaction and optimize operational efficiency. As gesture control continues to develop, it will play an even more crucial role in creating more intuitive, immersive, and seamless interactions between humans and technology, shaping the future of smart living and intelligent automation.
What is Gesture Control?
Gesture control refers to a technology that uses computer vision, deep learning algorithms, and various sensor technologies to detect, recognize, and respond to the movement of a user’s hands or other body parts. By capturing hand movements in real-time through cameras, depth sensors, or other devices, gesture control systems analyze these inputs and convert them into commands to control devices or trigger specific actions. Unlike traditional physical interfaces such as buttons or touchscreens, gesture control allows users to interact with systems in a contactless, intuitive manner, reducing dependency on physical devices and creating a more natural way of operating technology.
Smart Homes: Contactless Control and Personalized Services
In smart home environments, gesture control technology enables users to operate smart devices without physical contact, offering enhanced convenience and comfort. By integrating depth sensors and computer vision, users can control lighting, temperature, curtains, sound systems, and other connected devices with simple hand gestures. Whether adjusting the brightness of a light or the volume of a music system, gesture control makes it easier to personalize the home environment based on individual preferences.
Personalized Home Settings: Beyond basic control, gesture control systems can adapt to users' habitual movements. For instance, if a user tends to wave their hand to dim the lights, the system can recognize this gesture and automate the settings accordingly, creating a more intuitive and intelligent living space.
Healthcare: Contactless Monitoring and Medical Device Control
In healthcare, smart gesture control plays a vital role in enabling contactless monitoring and device control, particularly in scenarios where minimizing physical contact is essential. For elderly care or medical monitoring, gesture control allows patients or caregivers to trigger emergency alerts or adjust medical devices without touching them, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
Gesture-Triggered Emergency Alerts: In case of a medical emergency, a simple hand gesture can trigger an alert to notify caregivers or medical staff immediately, facilitating a faster response.
Contactless Medical Device Control: Medical professionals can also adjust devices like ventilators or infusion pumps through gesture control, ensuring safer and more hygienic operations in clinical settings.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Gaming: Enhanced Immersion and Interaction
The integration of gesture control in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) applications has brought about a more immersive and interactive experience. Players or users can control objects in the virtual world using natural hand movements, significantly enhancing the realism and engagement of the experience.
Virtual Object Interaction: In VR games, players can use gestures to interact with the virtual environment—grabbing, moving, or manipulating objects with a simple hand movement. This enhances interactivity and creates a deeper sense of presence in the virtual world.
Freeform Control and Precise Operation: With the ability to track hand gestures with high accuracy, users can perform intricate operations within the virtual space, such as fine-tuning objects or navigating complex environments, offering a level of precision that traditional controllers cannot match.
Smart Security: Efficient Monitoring and Security Management
In smart security systems, gesture control streamlines operations like adjusting surveillance cameras, triggering alarms, or activating emergency response systems. Security personnel can control devices and change camera angles or field-of-view remotely using gestures, significantly improving the efficiency of security management without needing to physically interact with the devices.
Remote Camera Control: By using gesture control, security staff can adjust the position and focus of surveillance cameras, providing enhanced coverage and the ability to monitor critical areas with precision.
Gesture-Activated Alarm Systems: In emergencies, security personnel can activate alarms or alert systems with a specific hand gesture, ensuring a rapid response to potential threats.
Industrial Applications: Optimizing Production Efficiency and Safety
In industrial environments, gesture control technology allows operators to remotely control machinery and production lines, improving operational efficiency and safety. By eliminating the need for physical contact with equipment, workers can adjust machine settings, such as speed, temperature, and pressure, through hand gestures.
Remote Adjustment of Industrial Equipment: In hazardous environments, such as high-temperature or high-pressure areas, workers can adjust production equipment without coming into direct contact with dangerous machinery, reducing the risk of accidents and improving worker safety.
Safe and Efficient Operations: Gesture control also enhances operational efficiency by enabling faster, more intuitive adjustments to production lines, ultimately reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Gesture-Controlled Access and Security Systems
Gesture control also plays a role in enhancing access control and identity verification systems in both residential and commercial buildings. By combining gesture recognition with facial recognition or other biometric systems, users can unlock doors or activate security systems without physically touching any devices.
Contactless Door Opening: A simple hand gesture can unlock a door, providing a seamless and secure way to enter a room or building without the need for physical contact with keypads or locks.
Secure and Efficient Authentication: Integrating gesture control with other security measures, like facial recognition or fingerprint scanning, creates a robust system for verifying identities while minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
Conclusion
Smart gesture control technology has immense potential across a wide range of industries, from smart homes and virtual reality to healthcare, security, and industrial automation. By combining advanced computer vision, deep learning algorithms, and sensor technologies, this technology enables intuitive, contactless interaction and enhances operational efficiency, safety, and user experience.
As the technology evolves, gesture control will play an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of human-machine interaction, offering seamless, immersive experiences across a variety of digital environments. In smart homes, gaming, industrial applications, and healthcare, gesture control will continue to drive innovation, delivering enhanced convenience, improved productivity, and greater safety, all while reducing physical contact and streamlining daily operations.
Field of View (FoV) and Time of Flight (TOF) in Gesture Control
Field of View (FoV) is crucial in gesture control systems as it determines the range in which gestures can be detected by sensors. The broader the FoV, the more gestures can be recognized from various angles and distances, enhancing the system’s flexibility.
Time of Flight (TOF) technology is often integrated into gesture control systems to measure the distance between the sensor and the user’s hand, allowing for precise 3D mapping of hand movements. This technology improves the system’s responsiveness and accuracy in real-time applications, enabling better gesture tracking and interaction in dynamic environments.
Synexens 3D Of RGBD ToF Depth Sensor_CS30
Our professional technical team specializing in 3D camera ranging is ready to assist you at any time. Whether you encounter any issues with your TOF camera after purchase or need clarification on TOF technology, feel free to contact us anytime. We are committed to providing high-quality technical after-sales service and user experience, ensuring your peace of mind in both shopping and using our products.
-
Posted in
CS30






